
You are in charge of the cake for your daughter's birthday and have decided the cake will have one candle for each year of her total age. When she blows out the candles, she'll only be able to blow out the tallest ones. Your task is to find out how many candles she can successfully blow out.
For example, if your daughter is turning 4 years old, and the cake will have 4 candles of height 4, 4, 1, 3, she will be able to blow out 2 candles successfully, since the tallest candles are of height and there are such candles.
Input: An array containing height of candle [4,4,1,3]
Output: Print the number of candles that can be blown out. 2
Explanation: We have one candle of height 1, one candle of height 2, and two candles of height 3. Your daughter only blows out the tallest candles, meaning the candles where height=3. Because there are 2 such candles, we print 2.

Given five positive integers, find the minimum and maximum values that can be calculated by summing exactly four of the five integers. Then print the respective minimum and maximum values as a single line of two space-separated long integers.
For example, arr=[1,3,5,7,9] . Our minimum sum is 1+3+5+7 and our maximum sum is 3+5+7+9. We would print 16 24

A monkey man caught inside a jail. He can jumps across the wall. He can jump 'X' meters, but due to slippery walls he falls 'Y' meters after each jump. To escape from jail, he has to cross 'N' number of walls, where height of each wall is given in an array.
Write a program to find total number of jumps, he has to make, to escape
Input Format
Your function will take three arguments, where:
Argument 1: An integer depicting X, which he can jump
Argument 2: An integer depicting Y, which he falls
Argument 3: An array of N integers having the height of each wall.
Constraints
1<=X<=109
1<=Y<=105
Output Format
Your program should return total number of jumps required to escape.
Sample Test Case
Test case 1
Sample Input 10 1 1 10
Sample Output 1
Explanation
Here monkey man can jump 10 meters high, but slides down by 1 meter. He has 1 wall to jump and the height of the wall is 10 meters. Since he jumps 10 meters in the first attempt he cross the wall easily in the first attempt only.
Test case 2
Sample Input 5 1 2 9 10
Sample Output 5
Explanation
Here, the monkey man can jump 5 meters high, but slides down by 1 meters. He has 2 walls to jump and the walls are 9 and 10 meters hight respectively.
While crossing the first wall, he takes 2 attempts, because during the first attempt he jumps 5 meters but slides down by 1 meters since he didn't cross the wall. In the next attempt he jumps 5 more meters from that position and this time he doesn't slide because he crossed the wall in this attempt because 4+5=9 and 9 meters is the actual height of the wall.
Similarly, while crossing the second wall, he takes 3 attempts because during his second attempt on this wall, he silides down by 1 meters since 4+5=9 and the height of the wall is 10 meters. During his third attempt, he was able to escape.
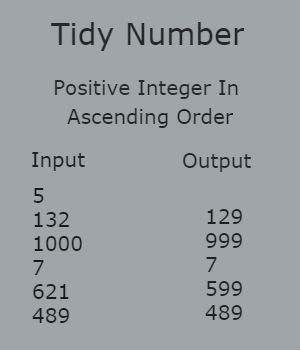
Ananya likes to keep things tidy. Her toys are sorted from smallest to largest and pencils are sorted from shortest to longest. One day, when practicing her counting skills, she noticed that some integers, have their digits sorted in non-decreasing order. She calls 8, 123, 555, and 224488 as numbers tidy. Numbers that do not have this property, like 20, 321, 495 and 999990, are not tidy.
She just finished counting all positive integers in ascending order from 1 to N. What was the last tidy number she counted?
Input
The first line of the input gives the number of test cases, T. T lines follow. Each line describes a test case with a single integer N, the last number counted by Ananya.
Output
For each test case, output is the last tidy number counted by Ananya.
1 ≤ T ≤ 100.
Sample Input:
5
132
1000
7
621
489
Sample Output:
129
999
7
599
489